In a world increasingly reliant on technology, the demand for efficient and reliable network connectivity has never been higher. When it comes to connecting devices to a network, there are two main options: wired and wireless. While wireless technology has gained popularity in recent years, many still argue that wired connections are superior. In this article, we will explore the advantages and disadvantages of both wired and wireless network cabling to determine which is better suited for different scenarios.
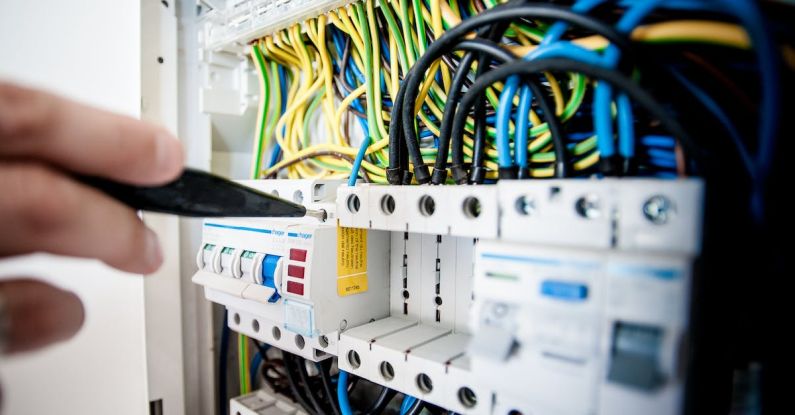
Wired Network Cabling: The Reliable Choice
Wired network cabling involves physically connecting devices to a network using cables. This traditional method of connectivity has been around for decades and has proven to be highly reliable. Here are some key advantages of using wired network cabling:
1. Speed and Stability: Wired connections offer faster and more stable network speeds compared to wireless connections. With no interference from other devices or obstacles, wired connections provide consistent and high-speed data transfer.
2. Security: Wired connections are generally more secure than wireless connections. Wireless networks can be susceptible to unauthorized access and interference, while wired connections are less prone to such risks. This makes wired connections ideal for businesses dealing with sensitive information.
3. Longevity: Wired connections have a longer lifespan compared to wireless connections. Wireless technology is constantly evolving, and older devices may not be compatible with newer wireless standards. In contrast, wired connections are backward compatible, ensuring long-term compatibility.
Wireless Network Cabling: The Convenient Choice
Wireless network cabling uses radio frequency signals to transmit data between devices without the need for physical cables. This method of connectivity offers several advantages that make it an attractive choice for certain situations:
1. Mobility: Wireless connections provide the freedom to connect devices from anywhere within the network’s coverage area. This flexibility is particularly beneficial in environments where mobility is essential, such as offices with hot-desking or homes with multiple devices.
2. Easy Installation: Setting up a wireless network is generally easier and quicker than running cables for a wired network. This can save time and reduce costs, especially in situations where running cables is impractical or disruptive.
3. Scalability: Wireless networks are highly scalable, allowing for easy expansion and addition of devices without the need for additional cables. This makes wireless networks suitable for environments that require frequent changes or have a high number of devices.
Choosing the Right Option
When deciding between wired and wireless network cabling, it is essential to consider the specific needs of your environment. Here are some factors to consider:
1. Speed and Reliability: If your network requires consistently high-speed and reliable connectivity, wired cabling is the better choice. This is particularly crucial for businesses that rely heavily on data transfer or have critical applications.
2. Mobility and Flexibility: If mobility and flexibility are essential, wireless cabling is the way to go. This is ideal for environments where devices need to move freely or where running cables is impractical.
3. Security and Privacy: If you handle sensitive data or require a high level of security, wired connections offer better protection against unauthorized access. However, wireless networks can still be secured with proper encryption and security measures.
In conclusion, both wired and wireless network cabling have their pros and cons. Wired connections excel in speed, stability, and security, making them ideal for environments where reliability is paramount. On the other hand, wireless connections offer convenience, mobility, and scalability, making them suitable for situations that require flexibility. Ultimately, the choice between wired and wireless network cabling depends on the specific needs of your environment and the trade-offs you are willing to make.