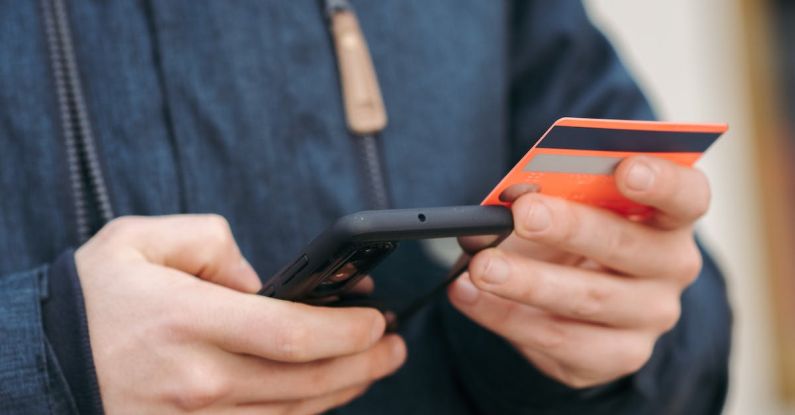
In an era where technology is rapidly advancing, the use of smartphone payment apps has become increasingly popular. People can now conveniently make payments for goods and services with just a few taps on their smartphones. However, with the rise of cybercrime, concerns about the security of these payment apps have also emerged. This article will delve into the security measures employed by smartphone payment apps and assess how secure they truly are.
Authentication and Encryption: The First Line of Defense
One of the primary security measures used by smartphone payment apps is authentication. Before a user can access their account, they are required to provide a unique password or use biometric authentication methods such as fingerprints or facial recognition. This initial layer of security ensures that only authorized individuals can access the app and make transactions.
Furthermore, to protect sensitive user data during transmission, smartphone payment apps employ encryption techniques. These apps use advanced encryption algorithms to convert user data into an unreadable format, making it nearly impossible for hackers to intercept and decipher the information.
Secure Data Storage: Safeguarding User Information
Smartphone payment apps understand the importance of protecting user information, and as such, they implement robust security measures for data storage. User data, such as credit card details and personal information, are stored in highly secure servers or the cloud, using encrypted storage methods. This ensures that even if a hacker manages to breach the app’s security, the stored data remains encrypted and inaccessible.
Tokenization: Preventing Data Breaches
Tokenization is another security feature employed by smartphone payment apps. When a user makes a payment, their credit card information is replaced with a unique token. This token is then used for the transaction, while the actual card details are securely stored in the app’s servers. This process prevents sensitive card information from being exposed during transactions, significantly reducing the risk of data breaches.
Fraud Detection and Prevention: Staying One Step Ahead
To combat fraudulent activities, smartphone payment apps utilize advanced fraud detection and prevention mechanisms. These apps analyze user behavior, transaction patterns, and location data to identify suspicious activities. If any irregularities are detected, the app can flag the transaction as potentially fraudulent and prompt additional verification steps.
Additionally, some apps employ machine learning algorithms that continuously learn from user behavior and transaction history. This enables the app to recognize and flag any unusual or unauthorized transactions, providing an extra layer of security.
Third-Party Audits and Compliance: Maintaining Trust
To maintain trust and ensure the security of their payment apps, providers often undergo third-party audits and comply with industry regulations. These audits assess the app’s security infrastructure, data storage practices, and adherence to privacy laws. Compliance with industry standards such as Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) further demonstrates a commitment to data security and provides assurance to users.
Conclusion: Embracing Convenience Without Sacrificing Security
Smartphone payment apps have revolutionized the way we make payments, offering convenience and efficiency. While concerns about security may arise, the app developers have implemented various measures to safeguard user data and prevent unauthorized access.
Authentication, encryption, secure data storage, tokenization, fraud detection, and compliance with industry regulations are some of the key security features employed by smartphone payment apps. These measures work together to create a robust security infrastructure, providing users with peace of mind when making transactions.
It is essential for users to stay vigilant and follow best practices to further enhance the security of their smartphone payment apps. This includes using strong and unique passwords, keeping their smartphones updated with the latest security patches, and being cautious of suspicious emails or links.
Overall, smartphone payment apps have made financial transactions more accessible and convenient. As long as users remain aware of potential security risks and take necessary precautions, the benefits of these apps can be enjoyed without compromising personal information or financial security.